Passageway For Optic Nerve
This surgery is designed to significantly lower the fluid within the eye to lessen the likelihood of pressure damage to the optic nerve which transmits vision from the eye to the brain. Intraocular intraorbital intracanalicular and intracranial.

Respiratory System Nurse Study Notes Medical Student Study Medical School Motivation
Like CN II the optic tract is paired.

Passageway for optic nerve. PPV and temporal-side single radial optic neurotomy is thought to create a barrier to fluid passage by creating scar tissue and is associated with fluid resolution in 86 of eyes. A passageway eg an opening puncture or incision is formed in the lamina cribosa or elsewhere to facilitate flow offluid from the posterior chamber of the eye to either a a subdural location within the optic nerve or b a location within the subarachnoid space adjacent to the optic nerve. It is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone.
A shunt is a small tube that creates an alternative passageway for the excess fluid to drain reducing the pressure in the eye. The optic nerve is a bundle of more than 1 million nerve fibers. Rods and cones are stimulated equally but the brain does not know how to process this confusing information so the resulting color is gray.
Passageway for oculomotor nerve. V1 V2 and V3 which are responsible for sensation in the face. They serve as a passageway for the optic nerve running from the eyeball to the optic chiasma The greater wings contain 4 openings.
The superior orbital fissure foramen rotundum foramen ovale and foramen spinosum. At dusk only cones are stimulated and they are equally stimulated. Neither rods nor cones are stimulated.
This optic nerve head was embedded with the superior tempo- ral tissue top left portion of the im- age closest to the plane and the in- ferior nasal tissue bottom right portion of the image farther back. The iris gives our eyes color and it functions like the aperture on a camera enlarging in dim light and contracting in bright light. The optic canal permits the passage of the optic nerve CN II and the ophthalmic artery into the bony orbit.
One of the cranial nerves the trigeminal V nerve serves most of the skin of the face and scalp. Fluid from the posterior chamber then drains into the optic nerve or directly into the subarachnoid space where it. Passageway for opthalmic nerve.
The optic tract is the intracranial continuation of the optic nerve. The aqueous is a clear watery solution in the anterior and posterior chambers. ODPs are rare cavitations of the optic nerve that may be asymptomatic or may be complicated by ODP-M leading to significant visual loss.
Passageway for maxillary nerve. The canal of Schlemm is the passageway for the aqueous fluid to leave the eye. Herpes zoster shingles a viral infection caused by varicella-zoster virus.
This bone houses the apparatus of the internal and middle ear. What is the clinical relevance of dermatomes. Passageway for optic nerve.
Passageway for abducens nerve. After its formation the nerve leaves the bony orbit via the optic canal a passageway through the sphenoid bone. The nerve supply in adjacent dermatomes overlaps somewhat.
Although no surgery can cure glaucoma permanently or reverse vision loss that has already occurred trabeculectomy is often effective in controlling pressure and reducing the risk of additional vision loss for. Once the retina senses the image it sends impulses to the optic nerve at the back of the eye. The three types of vision loss caused by optic nerve disorders are.
The 5th cranial nerve is divided into three divisions. Damage along the optic nerve pathway causes specific patterns of vision loss. Superior orbital fissure inside the orbit The greater wings also feature four foramina the foramen ovale foramen spinosum foramen Vesalli and foramen rotundum.
The optic nerve has four major portions. 6-8 Matching Questions 8-12 Allow cranial nerves that control eye movements to enter the orbit Anchor the pterygold muscles Passageway for optic nerve Forms parts of the middle cranial fossa dorsal walls of the orbits and external walls of. The aperture itself is known as the pupil.
One eye or one optic nerve is damaged. Thus the section plane in A proceeds through the dura d expanded arachnoid space a pia p retrolaminar optic nerve on lamina l central vascular tree cv prelaminar neural bundles pla Bruchs. One treatment option for glaucoma is a surgical procedure by which a small device called a shunt is inserted into the trabecular meshwork of the eye.
It is best to act quickly to prevent additional damage to the optic nerve and avoid future vision loss. The inferior orbital fissure formed by the greater wings and maxilla bones is a passageway for the maxillary nerve. Each spinal nerve contains sensory neurons that serve a specific predictable segment of the body called a dermatome derma- skin.
The pupil is the opening or aperture of the iris. Each is made up from temporal fibers arising from the retina of the ipsilateral eye as well as nasal fibers originating from the retina of the contralateral eye. The combination of all the cone colors is gray.
Passageway for vagus. Disease or injury can damage the optic nerve resulting in varying degrees of blindness. These cells in turn receive impulses from the photoreceptors of the eye the rods and cones.
Nerve signals travel along the optic nerve from each eye and send visual information to the brain. Passageway for trochlear nerve. This bone is wing-shaped and extends behind the eyes and forms part of the floor of the cranial vault.
Passageway for mandibular nerve. -tome thin segment Figure 1. The optic nerve is formed by the convergence of axons from the retinal ganglion cells.
Contiguous dermatomes overlap and each individuals exact dermatomal pattern is unique. Optic nerve pathway. Knowledge of dermatomes can aid in the diagnosis of disease.
Diagnosis of an ODP is achieved by fundus examination OCT of the optic nerve. Posterior to the lamina cribrosa optic nerve axons are. The optic nerve then transmits them to special areas in the brain which automatically flips the upside-down image so that it becomes upright again.
These cells in turn receive impulses from the photoreceptors of the eye the rods and cones. After its formation the nerve leaves the bony orbit via the optic canal a passageway through the sphenoid bone. What are the parts of optic nerve.
Knowing which spinal cord segments supply each dermatome makes it.

Pin By Catia Cilene Wennesheinier Da On Ideia Respiratory System Dog Vector Respiratory

Muscle Tissues Skeletal Cardiac Smooth Basic Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Textbook

The Skull Occipital Skull And Bones Sinusitis

La Vitamina C Es Esencial Para El Buen Funcionamiento De Nuestro Organismo Aqui Le Ensenaremos Mas Sobre Sus Beneficios Map

Iris Vintage Engraved Illustration Human Eye Dictionary Of Words And Things Larive And Fleur Engraving Illustration Eye Illustration Realistic Eye Drawing

Fascial Sheath Of Eyeball Tenon Extraocular Muscles Extrinsic Muscles Of Eyeball Superior Rectus Inferior Rectus M Anatomy Eye Illustration Dog Anatomy

Montessori Baby Shower Gift Set Five Pack Etsy Montessori Baby Baby Shower Gift Set Shower Gift Set

Respiratory System Medical School Inspiration Medical School Studying Medical Student Study

Pin On Research And Observation

Epiglottitis Ear Nose And Throat Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version Throat Anatomy Sinusitis Anatomy

Sphenoid Bone Supers View Axial Skeleton Skull Anatomy Axial
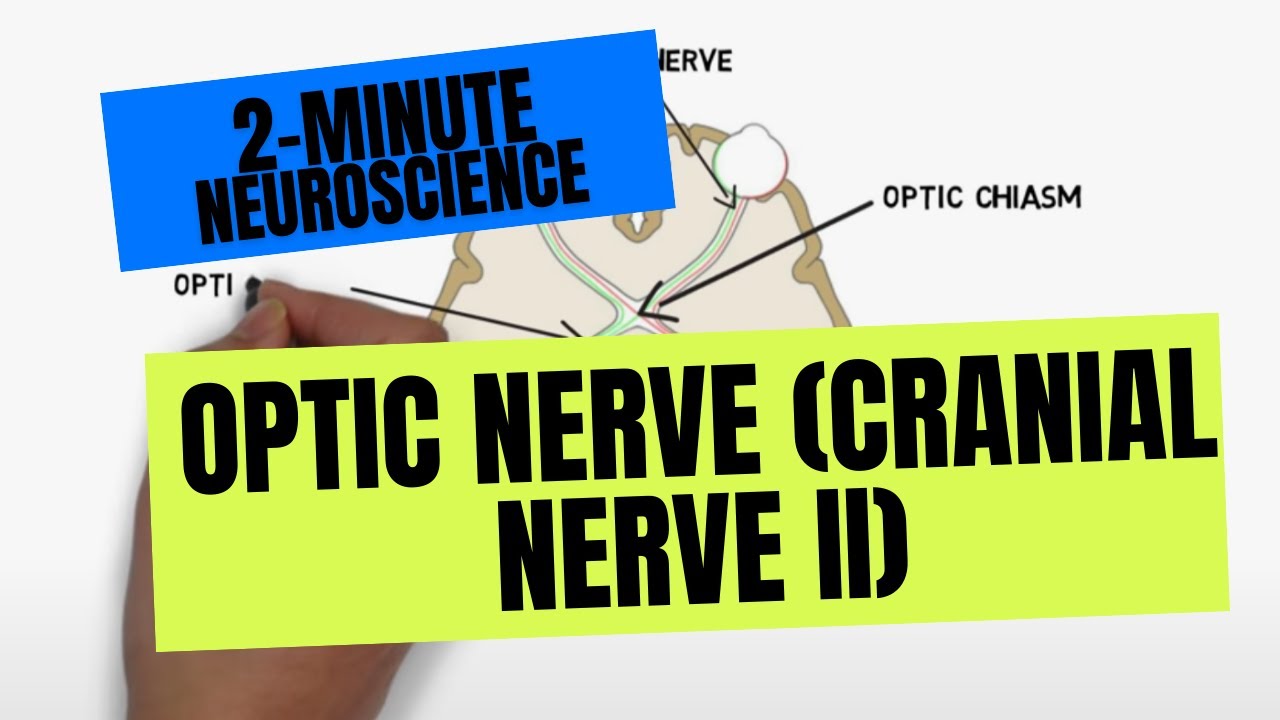
2 Minute Neuroscience Optic Nerve Cranial Nerve Ii Youtube

Optic Nerve Eye Anatomy Diagram Eye Study Eye Anatomy

Respiratory System Medical Student Study Medical School Studying Medical School Motivation

Synonyms Nervus Radialis Musculospiral Nerve Recommended Reading 1 Origin Terminal Branch Of Posterior Cord Of B In 2021 Radial Nerve Nerve Anatomy Sensory Nerves

Pin On Muslim S Culture Traditions Style Everything








Posting Komentar untuk "Passageway For Optic Nerve"